The Future of AI in Quality Engineering
Exploring how artificial intelligence and machine learning are transforming the landscape of software testing.
The Future of AI in Quality Engineering
Exploring how artificial intelligence and machine learning are transforming the landscape of software testing.
Introduction
In the last decade, software testing has shifted from being a back-office function to a critical enabler of business success. Faster releases, continuous delivery, and seamless user experiences have made quality engineering (QE) a boardroom priority.
Now, a new wave of transformation is underway. Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) are changing how we design, execute, and maintain test strategies. Instead of being reactive gatekeepers, QA teams are evolving into proactive quality partners—driven by data, prediction, and automation.
This blog explores how AI is shaping the future of Quality Engineering, the challenges that come with it, and what QA professionals need to do to stay ahead.
Why AI in Quality Engineering?
The traditional challenges in software testing include:
- High maintenance costs of automation scripts.
- Flaky tests that erode trust in automation.
- Slow feedback loops delaying releases.
- Limited coverage across rapidly changing platforms and devices.
AI addresses these pain points by:
- Learning from patterns in code and user behavior.
- Predicting defects before they hit production.
- Automating test generation and maintenance with minimal human intervention.
- Enhancing coverage by identifying high-risk areas intelligently.
Key Areas Where AI is Transforming QE
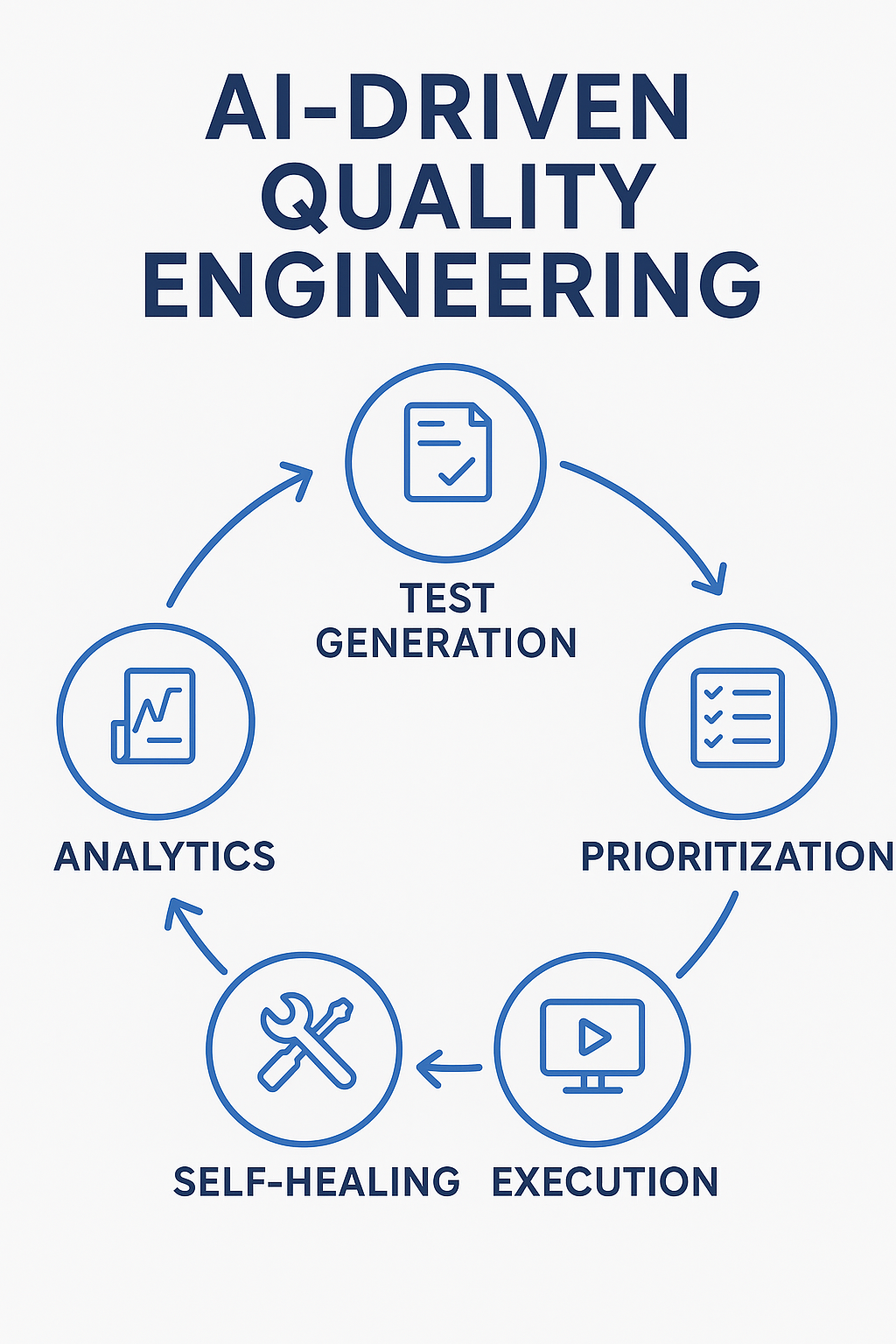
1. Test Case Generation
AI tools can analyze requirements, user stories, or even production logs to automatically generate relevant test cases.
Example: NLP-powered models that read Jira tickets or Figma designs and produce candidate test cases.
Impact: Faster onboarding for new features and reduced human effort in test design.
2. Self-Healing Test Automation
One of the biggest pain points in mobile and web automation is locator breakage. With AI:
- Tests auto-update when element identifiers change (using visual AI or contextual learning).
- Frameworks like Testim, Mabl, or Applitools use self-healing locators to minimize flakiness.
3. Defect Prediction Models
ML models can analyze historical data (commits, code churn, test results) to predict which modules are most likely to fail.
Impact: QA teams can prioritize high-risk areas and reduce regression suite execution time.
4. Intelligent Test Prioritization
Instead of running thousands of tests blindly, AI helps rank tests by importance based on:
- Code changes.
- User behavior data (e.g., most used app features).
- Business criticality.
Result: Reduced execution time with maximum risk coverage.
5. Visual Testing with AI
AI-based visual validation tools detect UI inconsistencies that human testers often miss.
- Can spot pixel-level differences, layout shifts, and responsiveness issues across devices.
- Tools like Applitools Visual AI are becoming mainstream.
6. Natural Language Test Automation (NLTA)
Testers write scenarios in plain English, and AI converts them into executable scripts.
Example: “Login as a valid user and verify balance screen” → converted into Appium/Selenium code automatically.
Benefit: Makes automation more accessible to non-technical testers.
Real-World Use Cases
- E-commerce: Predicting checkout flow defects by analyzing user journeys.
- Banking: AI-powered fraud detection tests integrated into QA pipelines.
- Healthcare: Ensuring compliance and accuracy in patient data handling using ML-driven validation.
- Gaming/Media: Visual AI checking screen rendering consistency across devices.
Benefits of AI in Quality Engineering
- Reduced Test Maintenance: Self-healing reduces manual intervention.
- Faster Time-to-Market: Prioritized, AI-driven tests mean quicker release cycles.
- Enhanced Accuracy: AI identifies defects that traditional scripts might miss.
- Data-Driven QA Strategy: Predictive analytics helps focus on risk areas.
- Improved Collaboration: NLTA bridges the gap between business stakeholders and technical QA teams.
Challenges and Limitations
- Data Dependency: AI models need large amounts of historical test data to learn effectively.
- Bias in Predictions: If past test data is skewed, AI may prioritize wrongly.
- Adoption Resistance: Teams may resist changing from traditional methods.
- Cost & Complexity: AI-based tools can be expensive and require expertise.
- Over-Reliance: AI should augment, not replace, human judgment.
How QA Professionals Can Prepare
- Upskill in AI & Data Literacy: Understanding how ML models work is essential.
- Experiment with AI-Powered Tools: Start small—try Applitools, Testim, or Mabl in parallel with existing frameworks.
- Adopt a Hybrid Approach: Combine rule-based automation with AI-driven insights.
- Collaborate with Dev & Data Teams: Evolve from “test executors” to “data-driven quality enablers.”
The Road Ahead
AI will not replace testers—it will augment their capabilities. The future of Quality Engineering lies in human-AI collaboration:
- Humans bring context, creativity, and judgment.
- AI brings speed, prediction, and adaptability.
Together, they’ll redefine quality practices:
- From reactive testing → to predictive quality assurance.
- From manual maintenance → to self-healing automation.
- From test execution → to continuous quality intelligence.
Conclusion
The future of Quality Engineering is intelligent, data-driven, and deeply collaborative. AI and ML won’t just make testing faster—they’ll make it smarter.
For QA leaders and engineers, the opportunity is clear: embrace AI early, experiment with tools, and evolve your mindset from “finding bugs” to “engineering quality.”
The organizations that succeed will not just deliver software faster—they will deliver trustworthy experiences that users can depend on.